
However, a closer look at the official announcement reveals that the upgrade represents more of a nominal increase in specifications than a major architectural overhaul.
The released 7000 series was already an impressive showcase for AMD’s Zen 4 processors and Radeon DNA 3 integrated graphics technology. On paper, the Ryzen 8000 series offers a similar foundation, even inheriting the same advanced 4nm manufacturing.
Core CPU configurations remain unchanged, with available options going up to 8 high-performance Zen 4 cores. Likewise, graphics options still excel on the Radeon 780M architecture featuring 12 compute units, and taper off from there. Essentially, AMD improved and complemented the existing formula rather than creating something completely new.
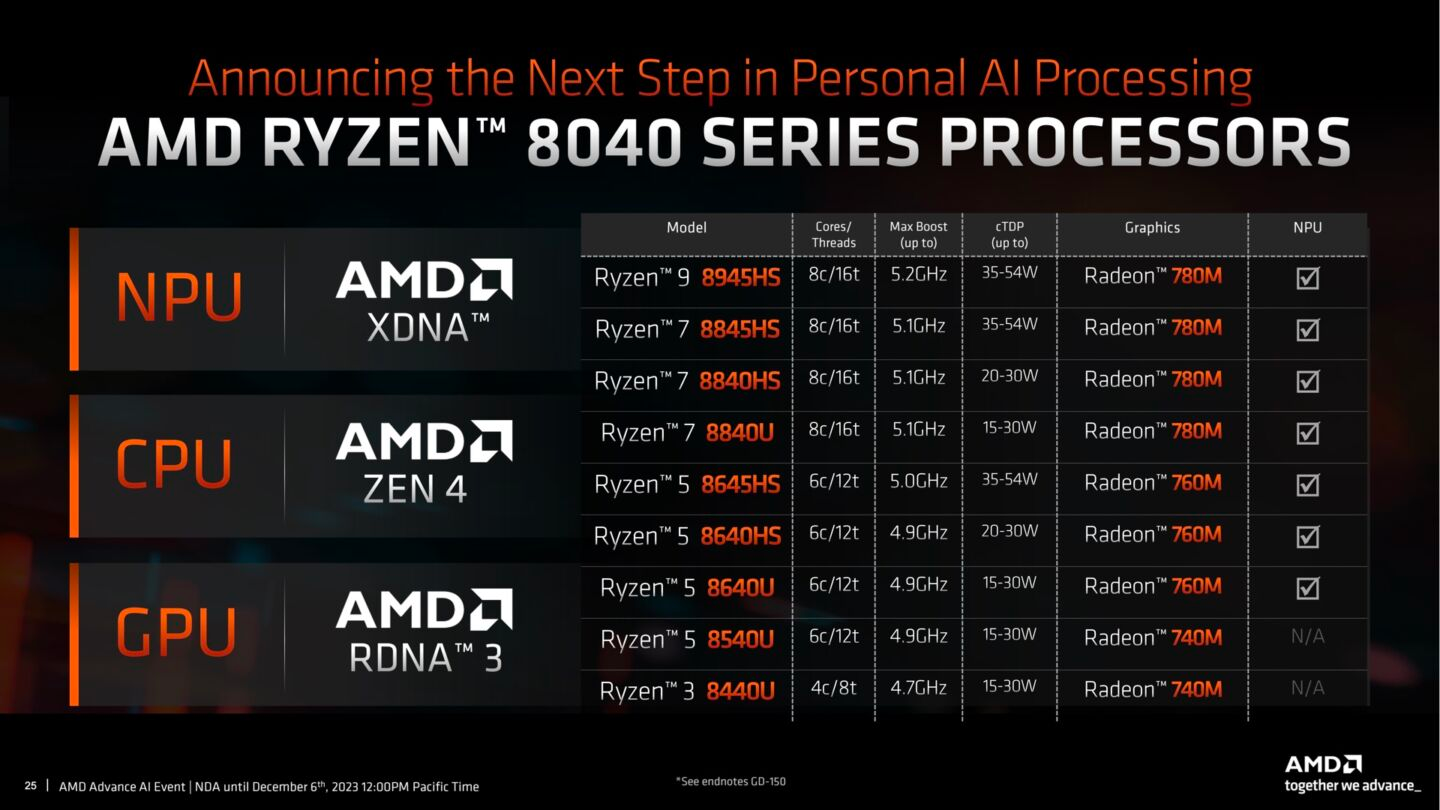
This is largely true when looking at clock speeds and thermal profiles as well. Without introducing vastly superior transistors or rearranging the architecture, dramatic jumps in frequency will be difficult. As such, the 8000 series ranges in speeds that are quite comparable to those achieved by the corresponding CPUs of the previous year.
Realistically, interested parties can expect modest single-digit percentage increases thanks to fine-tuned firmware and new drivers. But the huge gains made from completely renovated microstructures in the past have disappeared. AMD acknowledges that unmodified computing hardware prevents scaling up limits.
However, one area that shows significant improvements comes from the built-in accelerator AI hardware, now branded as 2nd Generation XDNA. By targeting emerging workloads like natural language processing, AMD was able to accelerate the processor’s machine learning capabilities by about 40% in some scenarios.
For devices that aim to operate as independent of the cloud as possible for privacy or practicality reasons, local engagement with AI becomes increasingly critical. AMD claims that tasks like background blur in video see a 1.4x increase compared to previous Ryzen chips. This is expected to help OEMs produce more attractive laptops with built-in smart features.

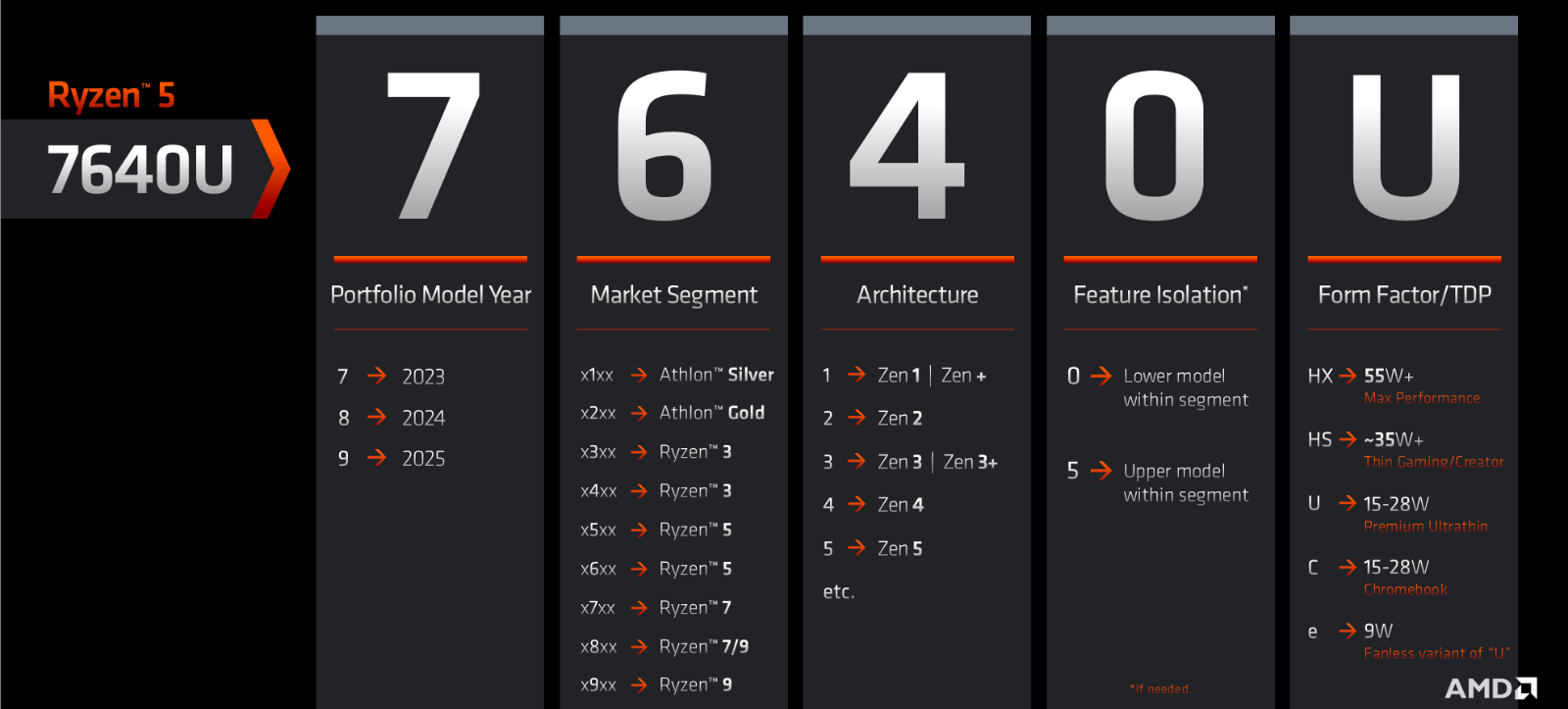
By tweaking the processor numbering system, AMD has been able to deftly maneuver around modest technological advances under the hood of the Ryzen 8000 series. Previously, large increases in the number accompanying a processor’s name were directly related to major changes in the microarchitecture. However, today’s version simply links the first number to the year of release.
In any case, the next-gen Zen 5, said to be codenamed Strix Point, is on the horizon for 2024, with AMD indicating we should expect much better performance.
-
2
-
3

“Total alcohol fanatic. Coffee junkie. Amateur twitter evangelist. Wannabe zombie enthusiast.”






More Stories
Is this what the PS5 Pro will look like? (Image)
Finally, Windows 11 24H2 update significantly boosts AMD Ryzen – Windows 11 performance
Heart Surgeon Reveals The 4 Things He ‘Totally Avoids’ In His Life