![An exciting discovery on Mars: A massive volcano, taller than Mount Everest, was hiding in plain sight [εικόνες] An exciting discovery on Mars: A massive volcano, taller than Mount Everest, was hiding in plain sight [εικόνες]](https://www.iefimerida.gr/sites/default/files/styles/facebook/public/2024-03/aris-ifaistio.jpg?itok=TaHUdLN4)
On the Red Planet, scientists have discovered a massive volcano, taller than Mount Everest, that had been hidden in plain sight for decades in one of the most famous regions on Mars, near the equator.
Located in the Noctis Labyrinthus (Night Labyrinthus) region of Mars, the volcano is about 1,200 kilometers long at the westernmost tip of Valles Marineris, the largest valley in our solar system and an extensive network of plateaus and trenches.
The volcano, provisionally named Noctis, has a height of 9,022 m – 8,849 m higher than Mount Everest – and extends over a vast area more than 450 km wide. In the same area there are three other giant volcanoes: Askrios Mons, Pavonis Mons and Arsia Mons.
The structure has been photographed several times since 1971
Although Noctis is larger in diameter than the other species, it appears to be more exposed to the elements and therefore not as tall. Because of this erosion, no one has observed it yet, although it has been photographed several times since 1971 by spacecraft orbiting Mars.
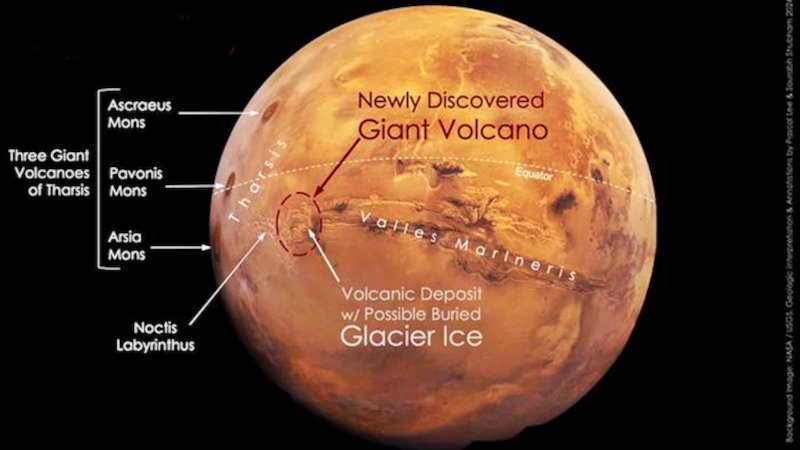
As researchers announced at the Lunar and Planetary Science Conference in Texas, the volcano has been active for a very long time on Mars, and in its southeastern part there are young, thin volcanic deposits, perhaps still under glacial ice.
“We were studying the geology of the area where we found the remains of a glacier last year when we realized we were inside a massive, heavily eroded volcano,” said Dr. Pascal Lee, a planetary scientist at the SETI Institute based at NASA's Ames Research Center. Center and lead author of the study.
New study: Mars' gravity may affect currents in Earth's oceans
NASA is looking for volunteers to live in a Mars simulation for a year
The central peak area is characterized by several high midpoints that form an arc, reaching a peripheral height and sloping away from the peak area, the researchers said. The gentle outer slopes radiate in different directions over a distance of more than 225 kilometers.
Near the center of the structure are the remains of a caldera – the remains of a collapsed volcanic crater that once housed a lava lake.
Researchers say this is a very important discovery as the combined presence of a volcano and a glacier in the same place provides a new location for a more detailed study of the geological evolution of Mars and the search for life by future robotics or manned missions. To the red planet.

“Avid problem solver. Extreme social media junkie. Beer buff. Coffee guru. Internet geek. Travel ninja.”




More Stories
In Greece Porsche 911 50th Anniversary – How much does it cost?
PS Plus: With a free Harry Potter game, the new season begins on the service
Sony set to unveil PS5 Pro before holiday season – Playstation