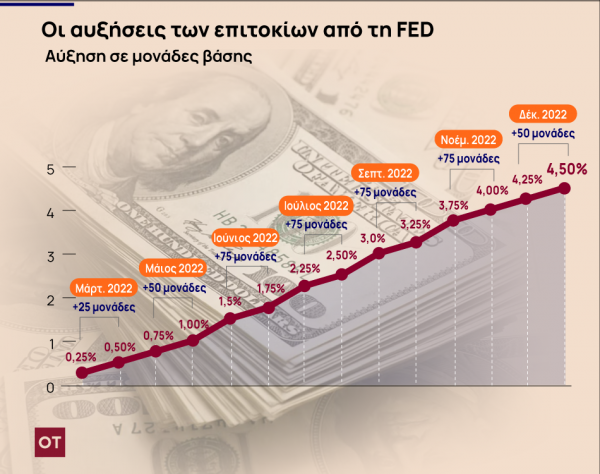
in a new increase of interest ratesthis time by 50 basis points, I went ahead Federal Reserve Bank From United States of America trying to restrain him inflation which “works” at a multiple of the 2% target. The prime lending rate is in dollars feed it It is now in the range of 4.25% to 4.50% and is the highest since 2007.
Fed Chairman Jerome Powell and other members have also indicated that they will continue to hike in 2023, albeit at a more subdued pace, to counter higher prices. The statement said the rate-setting committee expects that “continued increases” will be necessary to achieve monetary policy that “will be sufficiently restrictive to bring inflation back to 2% over time.”
Read also: Britain: Inflation rate at 10.7% in November
Fed officials now forecast that interest rates are expected to rise to 5.1% to 5.1% – up from 4.5% today after the new high – before putting the brakes on tighter monetary policy.
For this reason, the Fed expects that it will continue the increases in 2023 and estimates that reductions in borrowing costs are not expected before 2024.
The new increase was lower compared to the previous four sessions, when it was feed it He raised interest rates by 75 basis points on each. On the brakes you pressed feed it In terms of the severity of the increases, the better-than-expected data on inflation – however high it may be – and the fear that sustained large increases could deal a major blow to the US economy.
By steadily increasing the cost of borrowing, the Fed expects to reduce demand for expensive goods like homes and cars, which helps slow the economy and eases upward pressure on prices.
F officials wereEd They raised the benchmark rate by 0.75 percentage point on November 2, from nearly zero in early March. The Bank has raised interest rates by 75 basis points since 1994. It made four consecutive increases of this magnitude from June through October.
A few days ago, Jerome Powell indicated that the central bank would start to move less aggressively to see how price movements in the economy would evolve.
inflation factor
The US inflation rate was 7.1% in November on an annual basis, down from October’s 7.7% annual price hike, according to the latest data from the US Department of Labor. This was the slowest rate of growth in nearly a year and less than analysts had expected. The annual price index peaked at 9.1% in June, the largest increase since November 1981. However, inflation is still well above the Fed’s target of 2%.
The Consumer Price Index rose 0.1% last month compared to October, after rising 0.4% in October compared to September. Gasoline prices in the United States fell 2.0 percent. The cost of natural gas has also fallen, as has electricity prices. Food prices rose 0.5 percent, the slowest rate since December 2021, after rising 0.6 percent in October. The cost of food consumed at home rose 0.5%, driven by higher prices for fruits, vegetables, cereals and soft drinks. But meat, fish and eggs cost less in the United States now. “Prices are still very high,” US President Joe Biden said in a statement, adding that “things are getting better, and they are moving in the right direction.” The rise in consumer prices is now slowing in the United States as the cost of energy, used cars, Medicare and airline tickets falls.





More Stories
“Recycling – Changing the water heater”: the possibility of paying the financing to the institution once or partially
Libya: US General Meets Haftar Amid Tensions Between Governments
New tax exemption package and incentives for business and corporate mergers..