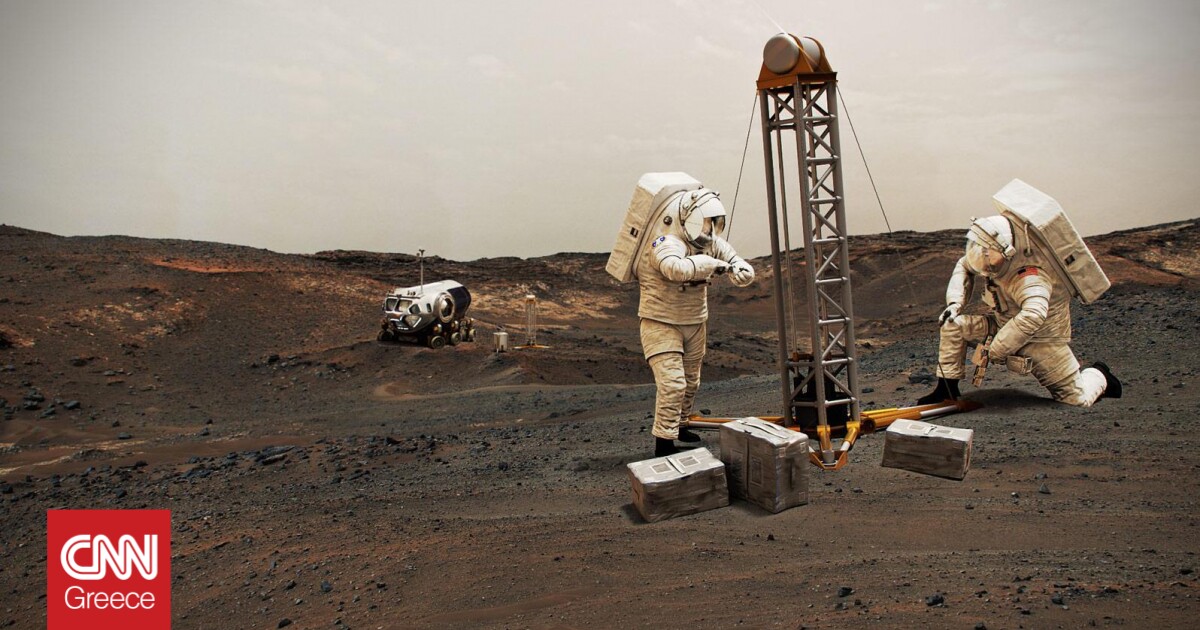

L’s first experience oxygen production On another planet completed a day MarsHaving exceeded its initial goals NASA It demonstrated capabilities that could help future astronauts explore the Red Planet.
the device Moxy (Mars Oxygen Resources In Situ Experiment) is the size of a microwave oven and is located on the rover perseverance.
The experiment began more than two years ago, that is, a few months after the rover landed on Mars. Since then, MOXIE has been in production 122 grams of oxygen, as much as a small dog breathes in 10 hours, according to NASA. The instrument works by converting some of the carbon dioxide abundant on Mars into oxygen.
At the peak of its efficiency, MOXIE Produced 12 grams of oxygen per hour with 98% purity or betterThis is twice the size of the goals set by NASA. On August 7, MOXIE ran for the sixteenth and final time, having completed all requirements.
“We are proud to support pioneering technology like MOXIE, which canConverting local resources into useful products “For future exploration missions,” said Trudy Curtis, technology demonstration manager for the Space Technology Mission Directorate at NASA Headquarters.
“With what this technology has proven in real-world conditions, we are one step closer to a future in which astronauts will live on the Red Planet.”
How does Moxie work?
The thin atmosphere of Mars is composed of… 96% of carbon dioxide. Moxy works Splitting carbon dioxide moleculesWhich contains one carbon atom and two oxygen atoms. separates oxygen molecules It emits carbon monoxide as a waste product. As gases move through the device, its system analyzes the purity and quantity of oxygen.
For the construction of the instrument was used Heat resistant materialssuch as a Gold and aerogel coatingThe conversion process requires reaching temperatures 798 degrees Celsius. These materials prevented heat from escaping and causing any damage to the vehicle.
Being able to convert carbon dioxide into oxygen can be beneficial in more ways than one. Bigger and better versions of devices like MOXIE could in the future power their life support systems breathable airbut also convert and store oxygen needed for Rocket fuel On the journey back to Earth.
“MOXIE’s impressive performance shows that it is possible to extract oxygen from the Martian atmosphere, oxygen that could help provide breathing air or rocket fuel for future astronauts,” NASA Deputy Administrator Pam Milroy said in a statement.
Carrying thousands of kilograms of rocket fuel and oxygen on the first flight from Earth to Mars would be incredible difficult and expensive It will mean less space on the spacecraft for other needs. Technologies like MOXIE can help astronauts to take advantage of the resources from their environment.
The lessons learned from the little MOXIE can now be used to create one Extensive system Which includes an oxygen generator, which will also be able to liquefy and store oxygen.
However, the next important step in this process is For testing on Mars and other technologies Which can help in exploring the planet, e.g tools And Housing materials.
With information from: The first experiment to produce oxygen on another planet has ended By Ashley Strickland, CNN

“Avid problem solver. Extreme social media junkie. Beer buff. Coffee guru. Internet geek. Travel ninja.”




More Stories
In Greece Porsche 911 50th Anniversary – How much does it cost?
PS Plus: With a free Harry Potter game, the new season begins on the service
Sony set to unveil PS5 Pro before holiday season – Playstation