The processors, which use the popular AM5 socket and are compatible with all AM5 motherboards on the market, are based on the new “Zen 5” architecture and, as with all the latest Ryzen desktop processors, are equipped with a certain number of CCDs (CPU Compound Dies). and cIOD (customer I/O die) where the former is manufactured using the 4nm method and the latter using the 6nm method.

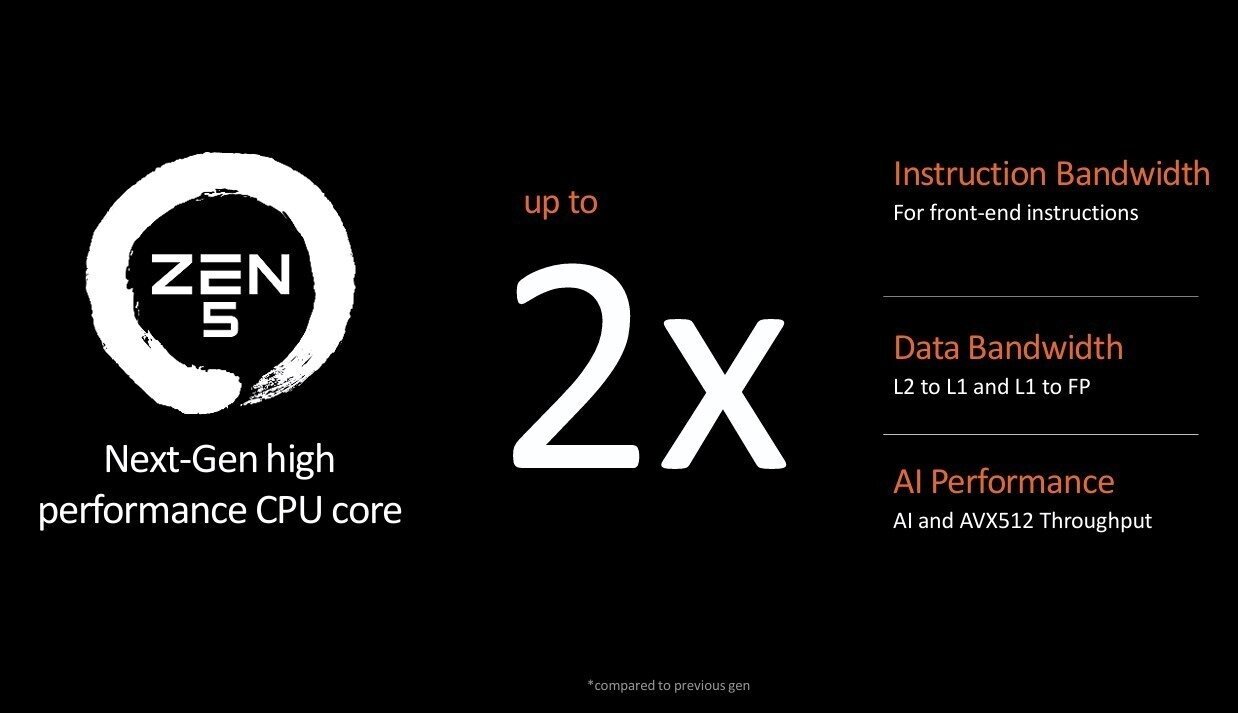
Thanks to various improvements in branch prediction, wider pipelines and vectors, a redesigned floating point arithmetic unit, increased bandwidth between different levels of latency, and a doubling of the performance of AI and AVX-512 workloads, AMD claims a 16% increase in IPC (instructions) per hour) compared to the performance of last generation Zen 4 processors.
AMD Ryzen 9000 series processors codenamed “Granite Ridge” consist of models with core counts ranging from 6 cores and 12 threads to 16 cores and 32 threads. As mentioned, the functional part of the processors, i.e. the cores are distributed in CPU Complex Dies or CCDs and models with 6 or even 8 cores have a single CCD design while those with 12 or even 16 cores have a dual CCD design. . Each CCD has one CCX cluster (CPU Core Cluster) comprising 8 cores of the “Zen 5” architecture with each incorporating 1MB of L2 cache and all cores sharing 32MB of L3 cache (L3).
Compared to the previous generation, there do not seem to be any differences in the space of the client input/output die (cIOD), which as mentioned is manufactured on a 6nm process and integrates, among other things, an RDNA 2 “graphics” with two computing units (CUs) for images/ Core functions, dual-channel DDR5 memory controller and 28-lane PCI-Express Gen 5 root pool.

AMD planned to release four Ryzen 9000 series models in the first phase with the 16-core Ryzen 9 9950X (16 cores/32 threads with maximum boost frequency of 5.7GHz and TDP of 170W) assuming the role of the flagship. Next up is the 12-core Ryzen 9 9900X (12 cores/24 threads) with an “enhanced” maximum frequency of 5.60GHz and a TDP of 120W. Right after that in terms of performance is the 8-core Ryzen 7 9700X (8 cores/16 threads) with a maximum boost frequency of 5.5GHz and a TDP of 65W. The last and most economical is the Ryzen 5 9600X hexa-core processor (6 cores/12 threads) that shows improved performance with a 5.40GHz overclocking and 65W TDP.
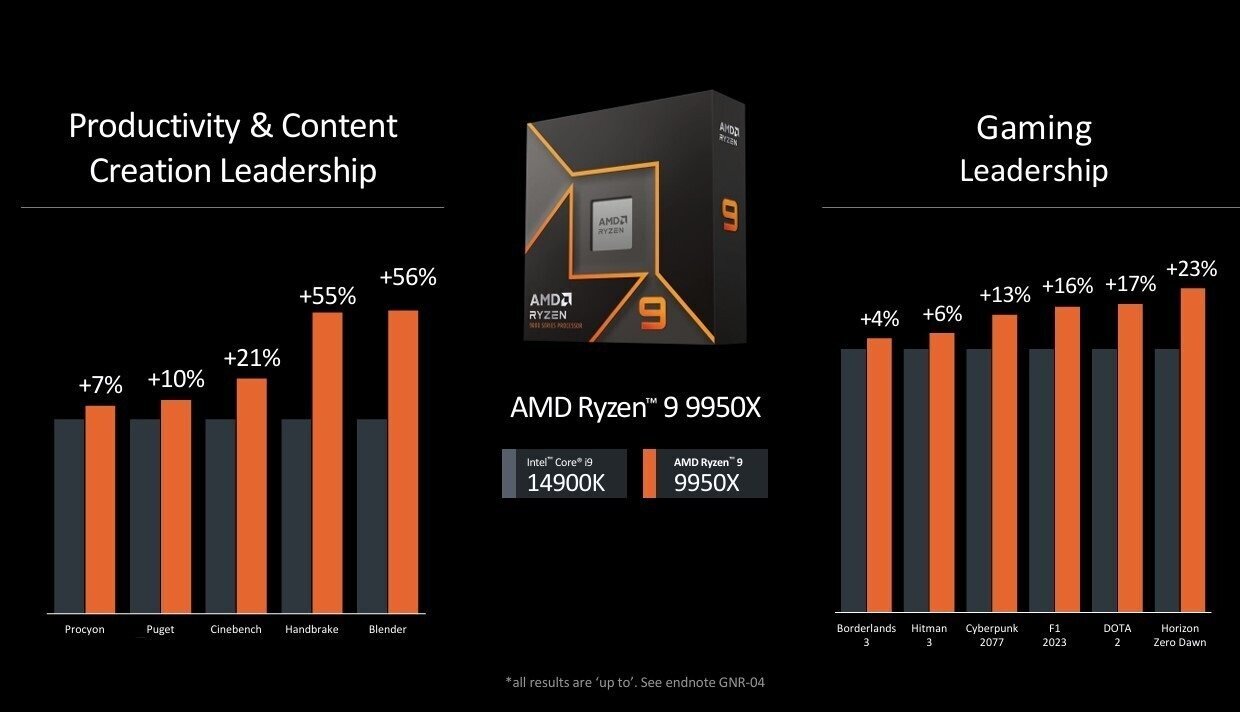
Comparing the Ryzen 9 9950X to the Intel Core i9-14900K, AMD claims it tops performance in content creation and productivity applications between +7% (in the UL Procyon benchmark for example) and 56% (in Blender).
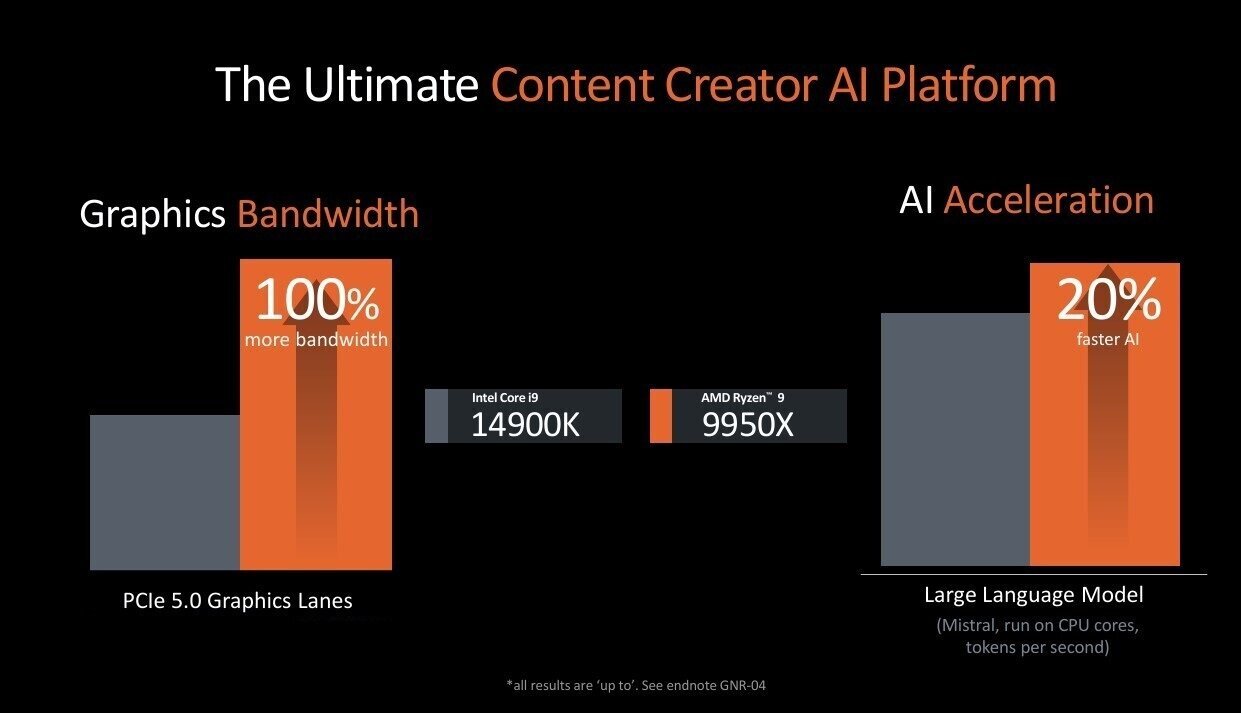
In games, the difference in performance ranges between 4% and 23%, and it is worth noting that the Mistral LLM device works 20% faster with the Ryzen 9 9950X compared to the Core i9-14900K.
The new processors take advantage of the familiar AM5 socket and are therefore still compatible with existing motherboards (BIOS upgrade may be required). However, AMD has announced the AMD X870E and X870 chipsets that complement its new platform with “standard” USB 4 connectivity for devices and PCI-Express 5.0 x16 for graphics cards. On the memory front, both chips allow for higher memory registers than in the past through AMD EXPO technology. On all cards, even for the x870.

It should be noted at this stage that AMD has not revealed the prices of the processors, but it promised to reveal them shortly before their launch in the markets in July 2024.
-

1





More Stories
In Greece Porsche 911 50th Anniversary – How much does it cost?
PS Plus: With a free Harry Potter game, the new season begins on the service
Sony set to unveil PS5 Pro before holiday season – Playstation