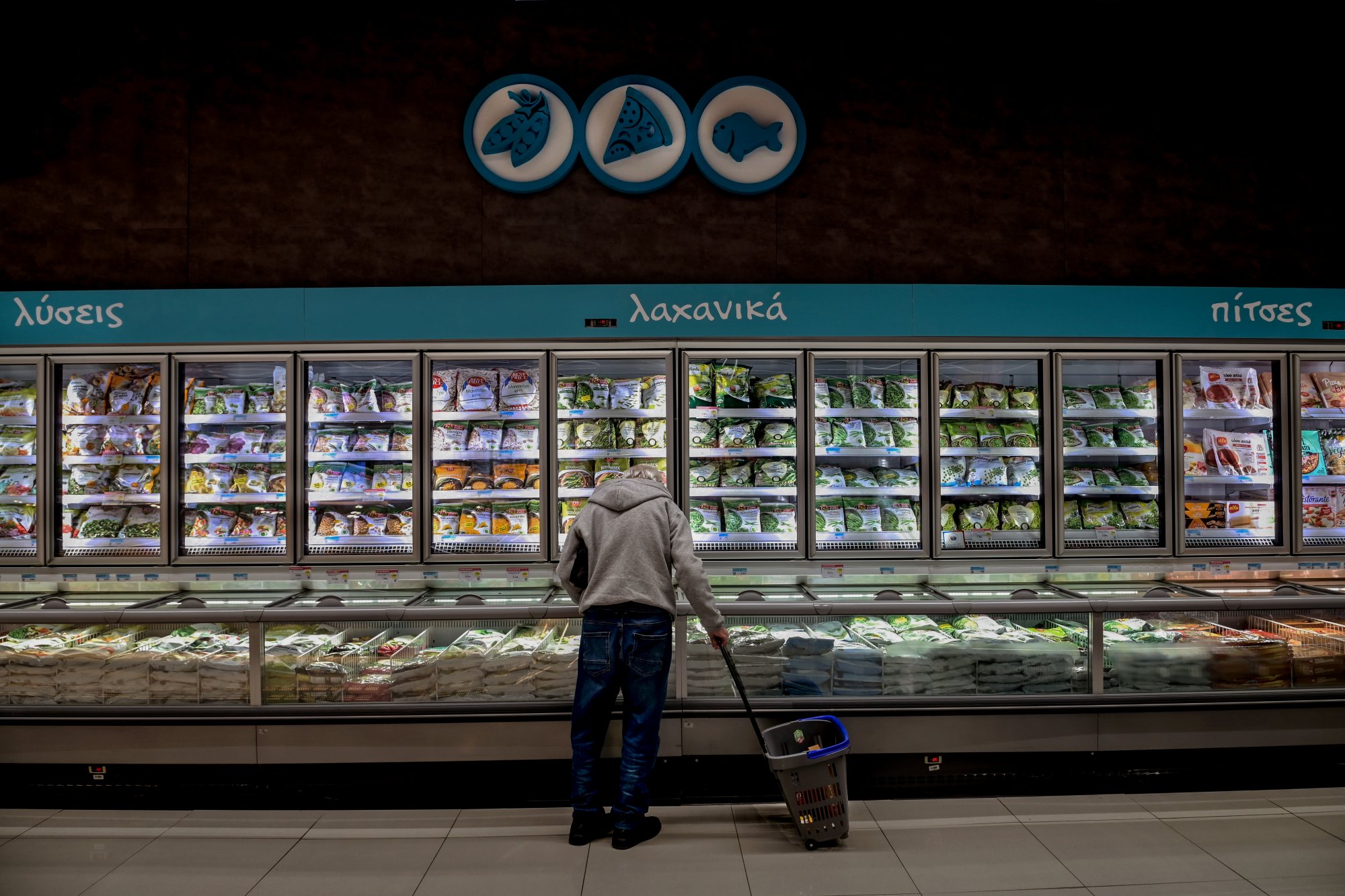

The data on the path of inflation that will be announced during the week by Eurostat is crucial because it will significantly influence the course of the Greek economy. Depending on the percentage that is announced, it is possible that we will see political interventions to contain prices, as households continue to experience the nightmare of their incomes shrinking, and fight an unequal battle for survival against those who benefit from them.
In Greece, inflation reached 3.1% in February, half a point higher than the eurozone and far from the European Central Bank's “sacred” target of 2%, which should be reached by mid-2024.
The inflation rate reached 2.6% in the euro area and 3.1% in Greece
Inflation is hoarse relative to the competition in the Greek economy
The Parliamentary Budget Office, among other things, examines all the data and, among other things, in its report includes “asterisks” and highlights what needs attention and is mainly related to inflation “multipliers”.
In the report there is special reference to the accuracy and high prices, which is considered hoarse not only for households but also for competition in the Greek economy.
In the scenarios he explains, he estimates that maintaining high inflation for some basic goods, such as food, burdens the costs of living for the most vulnerable households.
+7.46% in fresh fruits and vegetables
We remind you that as part of a targeted research conducted by the Consumer Goods Retail Research Institute (IELKA) exclusively in the channel of supermarket chains regarding inflationary pressures in food retail, the price path between February 2024 and February 2023 was examined.
The de-escalation (by 2.75%) in supermarket chains is a positive fact, but there are also some indicators (see Food) that inflation is still moving at high levels with fresh fruits and vegetables leading the race (+7.46%) due to rising costs. Production, extreme weather events, international raw material prices, and speculative phenomena.
Prices of fruits and vegetables are rising dramatically
As for the last part, it is distinctive that fruits and vegetables reach consumers at a price three times higher than the price at which the producer sells.
A typical example, as the Economic Postman wrote, are Merlin oranges that come out of the field for €0.15-0.25 per kilo and end up being sold in the supermarket for €0.80-0.85 per kilo. Accordingly, screaming apples leave producers at €0.60 per kilo and reach €1.80 on the shelf. Tomatoes whose production price ranges from 0.80 to 1 euro per kilo reach the consumer for 1.85 euros.
According to the report for the fourth quarter of 2023 presented on Monday (01/04) by the head of the Parliament's Budget Office, Yiannis Tsoukalas, it is necessary to intensify policy interventions in the direction of enhancing competition throughout the supply chain. These policies, if implemented correctly, could have led to a better result in achieving the goal of halting the rise in inflation.
“Greed” inflation.
With recent IMF research findings that Eurozone inflation as of the start of 2022 is 45% due to rising business profits, 40% to import prices, and only 25% to wage growth, the Parliamentary Budget Office is analyzing the data and conducting exercises on… Paper to analyze the scenario that might happen. Inflationary pressures are not abating.
In this scenario, as written, hyperinflation through aggressive demands for nominal wages to increase at a rate much higher than that generated by the sum of inflation and productivity would lead to a counterproductive, self-feeding spiral of increases that would ultimately lead to inflation rising by 1 percentage point . For the year 2024 to 3.9%.
Bell for increased wages and punctuality
In this case, the Greek economy would suffer losses in terms of international competitiveness, with consequent: a) decreased exports, b) decreased employment, real wages and private consumption, c) decreased investments.
This scenario, according to calculations, leads to GDP losses amounting to about 2.4 billion euros – equivalent to 1.2% of GDP – over three years.
far from 2%
The bureau's headline forecast puts the annual inflation rate at 2.9%.
Based on the unified consumer price index for February 2024, a slight decline in growth is observed, with a volume of 3.1%, slightly less than in January (3.2%). For the whole of 2023, the inflation rate reached 4.2%, while progress in its decline is evident since February 2023 when it reached 6.5%. According to the Bureau's analysis, this cooling trend is mainly due, as in the euro area, to the significant decline in energy costs which now has a negative contribution to the development of inflation.
Core inflation (excluding energy and unprocessed food) remains firmer at 3.3% for February 2024, while the same applies to the Eurozone, complicating the ECB's tightening monetary easing decisions.
Deviation of inflation from the target will have negative consequences for the entire economy
Food price inflation in particular persists, which, according to the Bureau's analysis, contributed 56% to overall annual inflation between January 2023 and January 2024, reducing the purchasing power of the incomes of mainly the most vulnerable households.
High inflation also risks strengthening inflationary expectations in households and businesses and poses a potential risk of the cancellation of these expectations and the consequent deviation of inflation from the 2.0% target set by the ECB in the medium term for the entire euro area. Deviation of inflation from the target will have negative consequences for the entire economy as mentioned above.

“Avid problem solver. Extreme social media junkie. Beer buff. Coffee guru. Internet geek. Travel ninja.”




More Stories
“Recycling – Changing the water heater”: the possibility of paying the financing to the institution once or partially
Libya: US General Meets Haftar Amid Tensions Between Governments
New tax exemption package and incentives for business and corporate mergers..