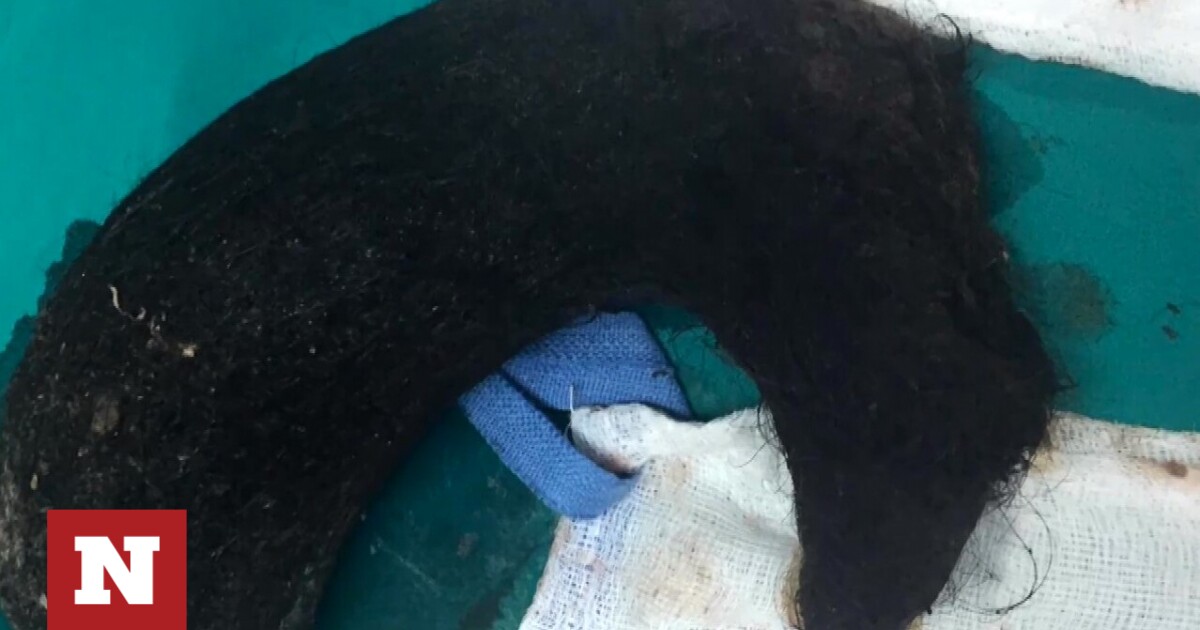
The amount of hair removed from the stomach of a 14-year-old girl in Thessaloniki is shocking. What is Rapunzel syndrome diagnosed by doctors, what are its symptoms and how is it treated?
700 grams of hair was removed from the abdomen of a 14-year-old girl Doctors from the Agios Loukas Clinic in Thessaloniki. The doctor who examined her for abdominal pain suspected that the girl had “Rapunzel Syndrome” when he saw the hair in her mouth. As it was established, the girl was eating threads from the curtains of her house, but her parents paid little attention to the cotton from the cotton fabric.
Check out the hair removed from the 14-year-old’s stomach:
14-year-old pediatric surgeon: One of the largest hairs identified and removed worldwide
Katerina Rammata, a pediatric surgeon who realized that the 14-year-old was suffering from Rapunzel syndrome, spoke to ERT about it. The “skeptical” movement led to the unraveling of the mystery of intense pain It was in the young woman’s stomach.
«This is secular, very familiar terminology. The Specific features A child from this incident His familyNot from someone from home Company Commonly used is and size, meaning its size Mass And the child’s history, it was overwhelming Informal and ambiguous. I mean, no one or anything from his history ever suspected that would be the case“, said the doctor politely.
According to Ms. Rammata, this hair follicle is one of the largest identified and removed globally.
«After diagnosing the problem, after treatment, going back and taking a history, the parents recalled some images of the child eating threads from curtains, swabs and cotton from hair already at the age of 2 years.“, said the pediatric surgeon.
symptoms
The use of the term Rapunzel syndrome first appeared in the literature in 1968.
Symptoms of the syndrome include:
- Small or large bowel obstruction
- Abdominal pain
- Nausea Vomiting
- Intestinal perforation
- Vitamin B12 deficiency
- Acute pancreatic necrosis
The reason
Both trichophagia and trichotillomania are classified under psychological disorders and usually occur together. In the case of trichophagy, the person eats or chews their hair. In trichotillomania, a person’s persistent behavior is observed where the person pulls hair from their head, eyebrows, eyelashes and generally all areas of the body that have hair. Because hair pulling becomes a compulsion for a person, it is included in obsessive-compulsive disorders. Usually, this pathological behavior is the sufferer’s way of relieving the stress they feel during the day.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis is made preoperatively, however, several aspects must be considered, such as the patient’s history of disorders such as trichophagia and trichotillomania.
Diagnosis of the syndrome is also done by endoscopy. A CT scan is recommended to determine its size and extent.
treatment
Because the human gastrointestinal tract cannot digest human hair, it may require surgery. It removes the mass by careful dissection from the stomach and duodenum. If the mass is small enough, it can be removed endoscopy.
Once the mass exceeds 20 cm, it should be removed by gastrotomy.
It is recommended to use general anesthesia with injection during hair removal. Long-term follow-up and psychiatric counseling are also recommended to prevent recurrence of the event.
Essentially, it is a patient referral Psychiatric treatment. Administration of drugs such as quetiapine (an antipsychotic drug) is indicated to control manic behavior in trichotillomania sufferers. So far, the factors that push the individual to this obsessive behavior – biological or environmental – have not been precisely determined. However, monitoring the person by a specialist can help the patient avoid relapse and identify the stress factors behind this condition (family, work, interpersonal relationships, school, etc.).
And more important Support A person coming from his family environment, but accepting the situation by the family.
Results
The outlook after surgery is promising. The success rate in removing the mass is over 90% and the complication rate is close to 10%. Relapse is extremely rare, but can occur if the patient does not follow psychotherapy or counseling.
Possible problems
- Obstructive jaundice
- Obstructive ileus
- Peritonitis
- Acute pancreatitis
Related news

. “Professional creator. Subtly charming web advocate. Unapologetic problem solver. Devoted student.”




More Stories
Criminal gang in Mykonos encouraged women into prostitution – how they set up romantic dates
Earthquake in Kavtos: “Too early to decide if it’s significant” – Valleys closed, risk of landslides
Halkidiki – Luna Park: SKAI Revelation – Discovered by the Expert