
Researchers at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) have developed a new type CementWhich could turn homes and streets into giant batteries and speed up the process of moving to them Renewable energy sources. The team incorporated a highly conductive material called… bloat With a mixture of water and cement and creating a building material that can also be used Supercapacitor.
Supercapacitors are very efficient at storing energy, but they are different from batteries. They charge and discharge much faster than one Lithium-ion battery They can withstand much greater charge and discharge cycles than batteries without significant degradation. However, they release the energy they store quickly, making them less useful for devices such as cell phones, laptops or electric cars, where a constant source of power is required for a long period.
However, says project leader Dr. Damian Stefaniuk, carbon-cement supercapacitors could make a major contribution to efforts to move humanity off carbon.
“If it can be scaled up, our technology could help solve an important problem –… Storage of renewable energy sources“, he told the BBC.
This type of cement can be used Road construction Which will be able to store energy in huge quantities. Buildings can be converted into huge complexes of electricity that can be generated with the help of photovoltaic panels. During the night, this energy will be stored in the foundations, according to the researcher.
At present, concrete hypercapacitor can store a slightly smaller amount of 300 watt hours per cubic meter – Enough to feed one 10 watt LED bulb lasts for 30 hours.
“The energy may seem small compared to conventional batteries, but a base of 30 to 40 cubic meters of concrete can cover the daily energy needs of a dwelling,” the researcher said.
“Given the widespread use of concrete around the world, this material has the potential to be highly competitive and useful in energy storage,” he added.
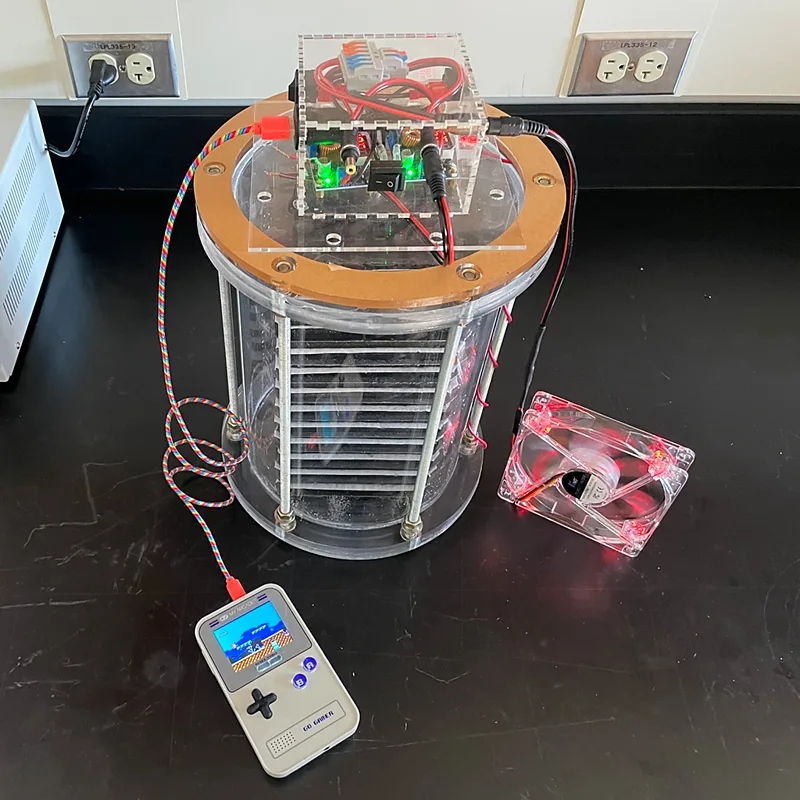

The research team now plans to build larger versions of the supercapacitor, including a 45-cubic-meter version that will be able to store about 10 kilowatt-hours of energy needed to power a home for a day.
Capacitors consist of Two electrically conductive panels Which are immersed in the electrolyte and separated by a membrane. In this particular case, the two panels were made of carbon black cement impregnated with potassium chloride. When a voltage is applied to the capacitor, positively charged ions from potassium chloride accumulate on the negatively charged plate. In contrast, the positively charged plate accumulated negatively charged ions. Because the membrane prevents the exchange of charged ions between the two plates, the separation of charges creates an electric field.
Although carbon cement supercapacitors can help reduce our dependence on lithium batteries, they still negatively impact the environment. Cement production calculations 5-8% of CO2 emissions Due to human activity around the world.
“This research opens up many interesting potential avenues,” Dr. Hans said. Michael Short, a specialist in sustainable engineering at Teesside University in the UK. “But more research is needed to meet the challenges of scaling up this technology and reducing its environmental footprint,” the scientist concluded.
source: BBC

“Avid problem solver. Extreme social media junkie. Beer buff. Coffee guru. Internet geek. Travel ninja.”




More Stories
In Greece Porsche 911 50th Anniversary – How much does it cost?
PS Plus: With a free Harry Potter game, the new season begins on the service
Sony set to unveil PS5 Pro before holiday season – Playstation