A US-made F-16 fighter jet, which the country had received a few weeks ago, has crashed in Ukraine.Its pilot, Oleksiy...
The possibility of one-time or partial repayment of financing to the organization is provided for in the amendment to the...
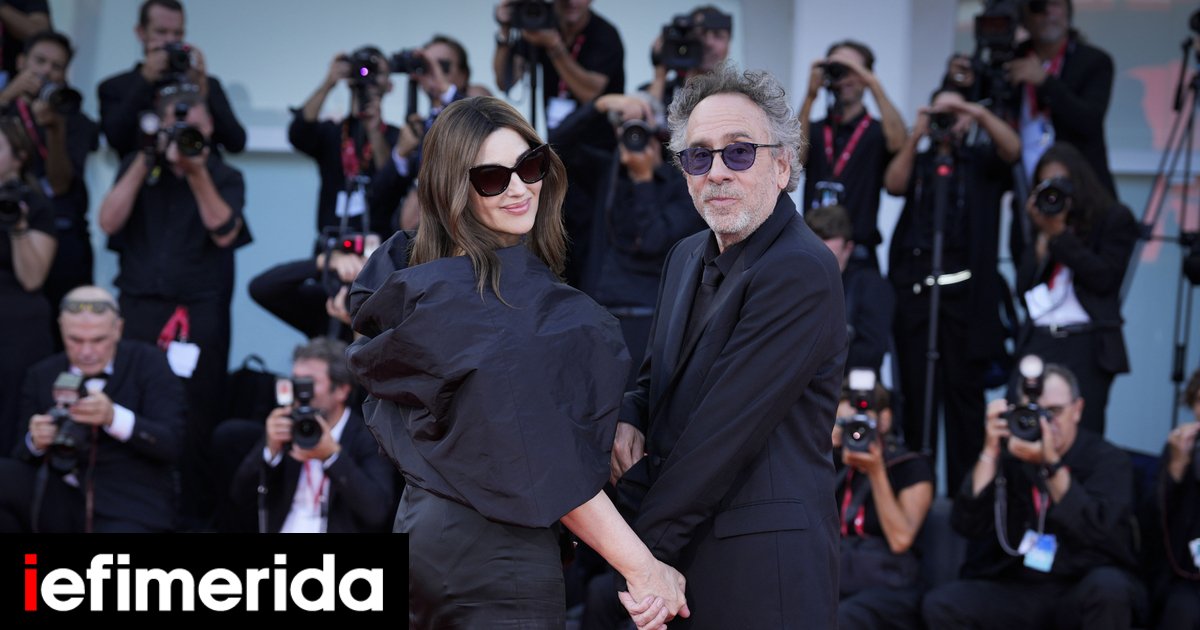
Monica Bellucci and Tim Burton arrived together in Venice to attend the 81st Venice International Film Festival, which is held...
Its commercial career began in Greece with the Porsche 911 Anniversary Edition, created to mark the 50th anniversary of the...
It's been a mess for the past 24 hours regarding the upgraded console. Sonythe Playstation 5 ProA trusted industry insider...
The three women were victims of a criminal human trafficking ring Mykonos2024 was discovered and recovered on the evening of...
According to the report, the player's offer was submitted three days ago. One of the names that fell on the...
Namibia plans to kill more than 700 wild animals Including elephants, zebras and hippos, and distributing meat to food insecure...
Gen. Michael Langley, who serves with the U.S. Central Command (CENTCOM) and Jeremy Bendett, the U.S. charge d'affaires in Tripoli,...
The concert he was scheduled to give Anna Vesey With him Antonis Remo And she has Eleni Foureira In Ioannina....