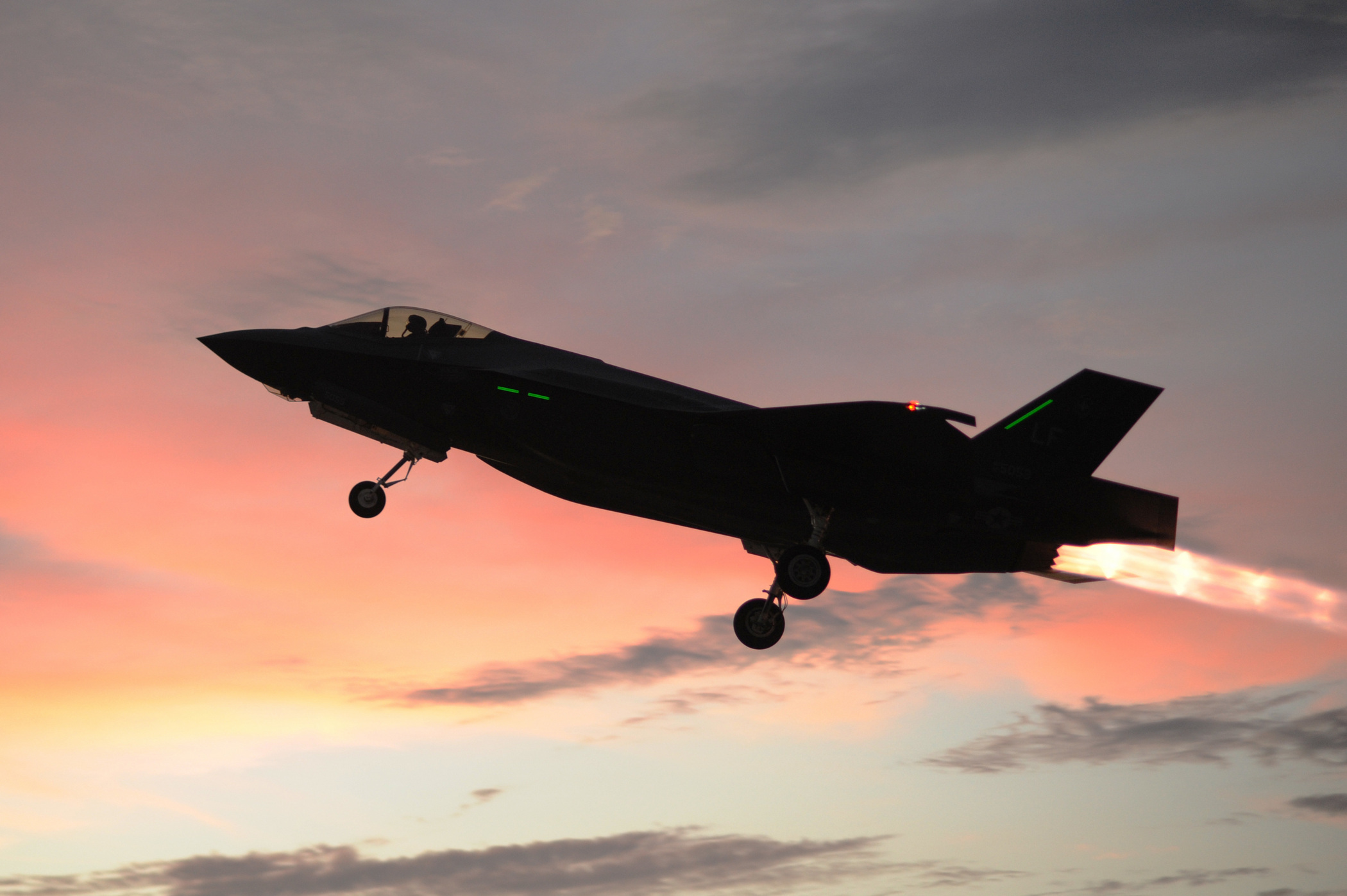

As we have said many times, the F-35 is designed to serve as a sensor suite over the operational domain, sharing information with friendly forces, thanks to its data fusion capability and its transport systems, MADL and Link 16.
F-35A: Greece No Surprises in JSF Club – There Was an Option for 20 More – When Will We Get Jets?
So, in ballistic threat testing several years ago, two of the F-35’s electronic systems were used, The AN/APG-81 active phased array radar and AN/AAQ-37 DAS electro-optical system have proven their ability to be used as early warning sensors against ballistic threats..
Thus, in a 2010 test, the DAS system, installed on a Northrop–Grumman BAC1-11 test aircraft, was able to detect a missile at successive stages of its trajectory, even during separation 1.Sh and 2Sh The field, as well as upon re-entry. What is even more impressive is that the range achieved exceeds 1,300 kilometers and this is due to the advanced algorithms of the system.
In June 2012, another test, in collaboration with NASA on behalf of the ATREX (Anomalous Transport Rocket Experiment) program, demonstrated the cooperative capability of the two sensors, DAS and APG-81, in detection, tracking and targeting functions, through multiple missile launches. In particular, the DAS system initially detected the target and then set the radar to track and target it. Two Terrier Improved Malemute suborbital test rockets, two Terrier Improved Orion rockets and one Terrier Oriole rocket were used in the tests.
Here’s to say that from Series 15 onwards, the F-35 will carry Raytheon’s improved EODAS SLS, and from Series 17, it will carry Northrop Grumman’s new AN/APG-85 active radar. So These improvements are expected to be introduced by Greek F-35s as well.

“Avid problem solver. Extreme social media junkie. Beer buff. Coffee guru. Internet geek. Travel ninja.”




More Stories
“Recycling – Changing the water heater”: the possibility of paying the financing to the institution once or partially
Libya: US General Meets Haftar Amid Tensions Between Governments
New tax exemption package and incentives for business and corporate mergers..